
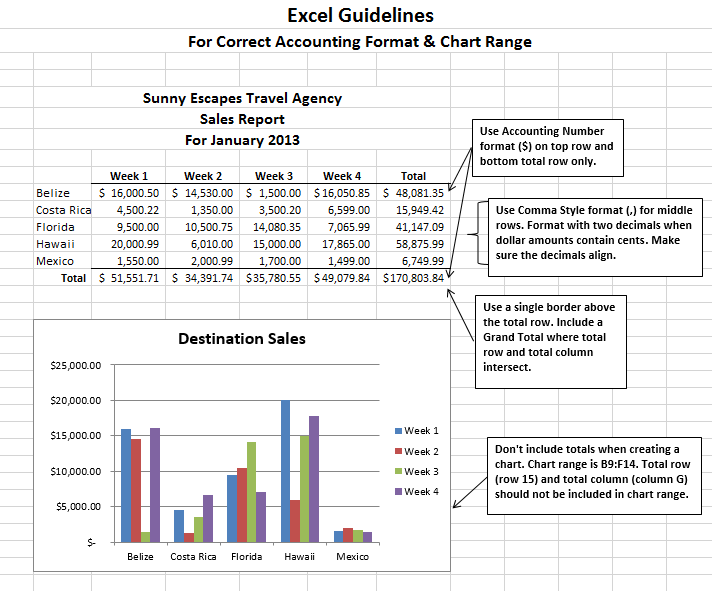
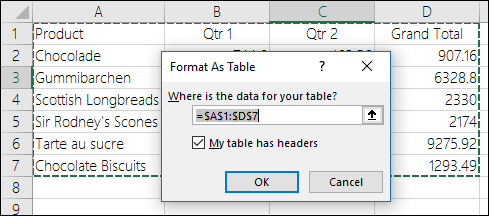
With the active cell inside your data range, go to the Insert tab in the ribbon and press the Table button found in the Tables section. Instead of letting Excel guess the range you can also select the entire range of data in this step. You’ll be able to confirm this range later on. Select any cell inside your data and Excel will guess the range of your data when creating the table. Create a Table from the RibbonĬreating an Excel Table is really easy. Each cell in the total row will have a drop down menu that allows selection of various summary formula. This row can contain text, formula or remain blank. If it’s enabled, it will be the last row of the table. By default, tables don’t include a total row but this feature can be enabled if desired. A table must contain at least one column. The body of a table can contain one or more rows and if you try to delete all the rows in a table a single blank row will remain. The body is where all the data and formulas live. Column headings must be unique in the table, they cannot be blank and they cannot contain formulas. It is the first row in a table and contains the column headings that identify each column of data. Throughout this post, I’ll be referring to various parts of a table, so it’s probably a good idea that we’re both talking about the same thing. This post will tell you about all the awesome features tables have and should convince you to start using them. Ok, so what’s so great about Excel Tables other than being a container to organize data? A lot actually. Without a table, the only thing relating the data is proximity to each other. Tables tell excel that all the data is related. Similarly, you might put all your customer data into one Excel table. In your house, you might put all your plates into one kitchen cupboard.
Imagine a house without any closets or cupboards to store your things, it would be chaos! Excel tables are like closets and cupboards for your data, they help to contain and organize data in your spreadsheets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
